
Baroque - V
Claude Lorrain
1600 – 1682
Claude Lorrain (c. 1600 – 23 November 1682) was a French painter, draughtsman and etcher of the Baroque era. He spent most of his life in Italy, and is one of the earliest important artists, apart from his contemporaries in Dutch Golden Age painting, to concentrate on landscape painting. His landscapes are usually turned into the more prestigious genre of history paintings by the addition of a few small figures, typically representing a scene from the Bible or classical mythology.
By the end of the 1630s he was established as the leading landscapist in Italy, and enjoyed large fees for his work. His landscapes gradually became larger, but with fewer figures, more carefully painted, and produced at a lower rate. He was not generally an innovator in landscape painting, except in introducing the sun and streaming sunlight into many paintings, which had been rare before. He is now thought of as a French painter, but was born in the independent Duchy of Lorraine, and almost all his painting was done in Italy; before the late 19th century he was regarded as a painter of the "Roman School". His patrons were also mostly Italian, but after his death he became very popular with English collectors, and the UK retains a high proportion of his works.
He was a prolific creator of drawings in pen and very often monochrome watercolour "wash", usually brown but sometimes grey. Chalk is sometimes used for under-drawing, and white highlighting in various media may be employed, much less often other colours such as pink. These fall into three fairly distinct groups. Firstly there are large numbers of sketches, mostly of landscapes, and apparently very often done at the scene; these have been greatly admired, and influenced other artists. Then there are studies for paintings, of various degrees of finish, many clearly done before or during the process of painting, but others perhaps after that was complete. This was certainly the case for the last group, the 195 drawings recording finished paintings collected in his Liber Veritatis (now in the British Museum). He produced over 40 etchings, often simplified versions of paintings, mainly before 1642. These served various purposes for him, but are now regarded as much less important than his drawings.[6] He painted frescoes in his early career, which played an important part in making his reputation, but are now nearly all lost.

Self-Portrait

Landscape with Merchants
c. 1630

The Campo Vaccino, Rome
-

Marine with the Trojans Burning their Boats
1643

Landscape with Cephalus and Procris Reunited by Diana
1645
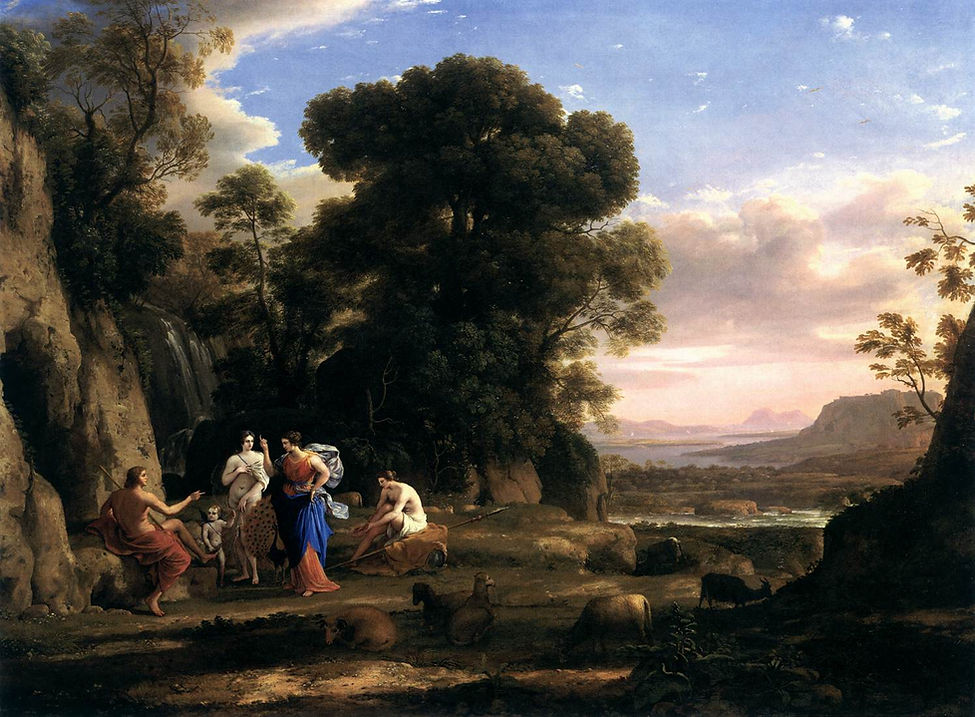

The Judgment of Paris
1645-46

The Rape of Europa
1655

Landscape with Acis and Galatea
1657

Landscape with the Rest on the Flight into Egypt
1666

The Expulsion of Hagar
1668

Landscape with Jacob Wrestling with the Angel
1672

Apollo and the Muses on Mount Helion (Parnassus)
1680

Landscape with Apollo Guarding the Herds of Admetus and Mercury stealing them
1645
Adriaen Brouwer
1605 – 1638
Adriaen Brouwer (c. 1605 – January 1638) was a Flemish painter active in Flanders and the Dutch Republic in the first half of the 17th century. Brouwer was an important innovator of genre painting through his vivid depictions of peasants, soldiers and other "lower class" individuals engaged in drinking, smoking, card or dice playing, fighting, music making etc. in taverns or rural settings. Brouwer contributed to the development of the genre of tronies, i.e. head or facial studies, which investigate varieties of expression. In his final year he produced a few landscapes of a tragic intensity. Brouwer's work had an important influence on the next generation of Flemish and Dutch genre painters. Although Brouwer produced only a small body of work, Dutch masters Peter Paul Rubens and Rembrandt collected it.

Portrait of Adriaen Brouwer by Anthony van Dyck
1631

A Boor Asleep

The Bitter Draught
c. 1635

The Back Operation
1635-36

Brawling Peasants
1634-37

Brawling Peasants
1634-37

The Card Players

Drunken Peasants
1620s

Feeling
c. 1635

Peasants Fighting
1631-35

Smoking Men
c. 1637

Village Scene with Men Drinking
1631-35

Tavern Scene
1635
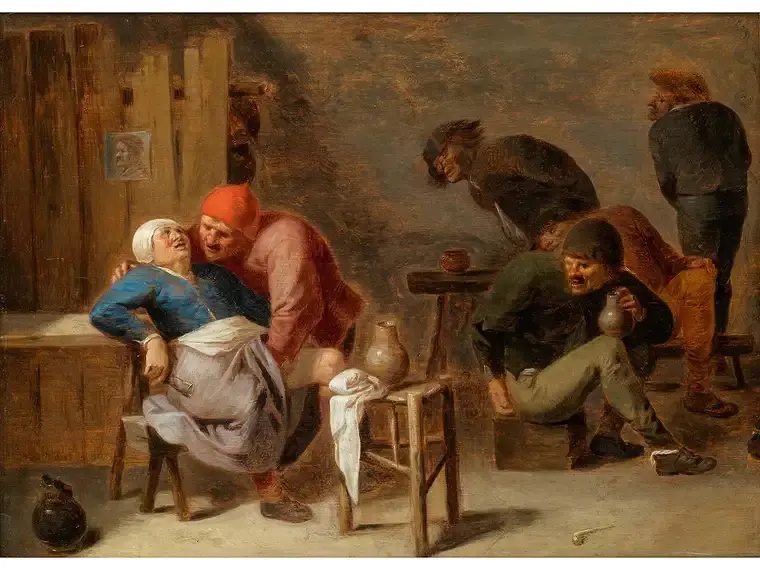

Tavern Scene

Peasants Carousing in a Tavern
Rembrandt
1606 – 1669
Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn (15 July 1606 – 4 October 1669), usually simply known as Rembrandt, was a Dutch Golden Age painter, printmaker, and draughtsman. An innovative and prolific master in three media, he is generally considered one of the greatest visual artists in the history of art. It is estimated Rembrandt produced a total of about three hundred paintings, three hundred etchings, and two thousand drawings.
Unlike most Dutch masters of the 17th century, Rembrandt's works depict a wide range of styles and subject matter, from portraits and self-portraits to landscapes, genre scenes, allegorical and historical scenes, biblical and mythological themes and animal studies. His contributions to art came in a period of great wealth and cultural and scientific achievement that historians call the Dutch Golden Age, when Dutch art (especially Dutch painting) was prolific and innovative.
Rembrandt never went abroad but was considerably influenced by the work of the Italian Old Masters and Dutch and Flemish artists who had studied in Italy. After he achieved youthful success as a portrait painter, Rembrandt's later years were marked by personal tragedy and financial hardships. Yet his etchings and paintings were popular throughout his lifetime, his reputation as an artist remained high, and for twenty years he taught many important Dutch painters.
Rembrandt's portraits of his contemporaries, self-portraits and illustrations of scenes from the Bible are regarded as his greatest creative triumphs. His approximately 40 self-portraits form an intimate autobiography. Rembrandt's foremost contribution in the history of printmaking was his transformation of the etching process from a relatively new reproductive technique into an art form. His reputation as the greatest etcher in the history of the medium was established in his lifetime.
Early life and education

Self-portrait

The Holy Family
1634
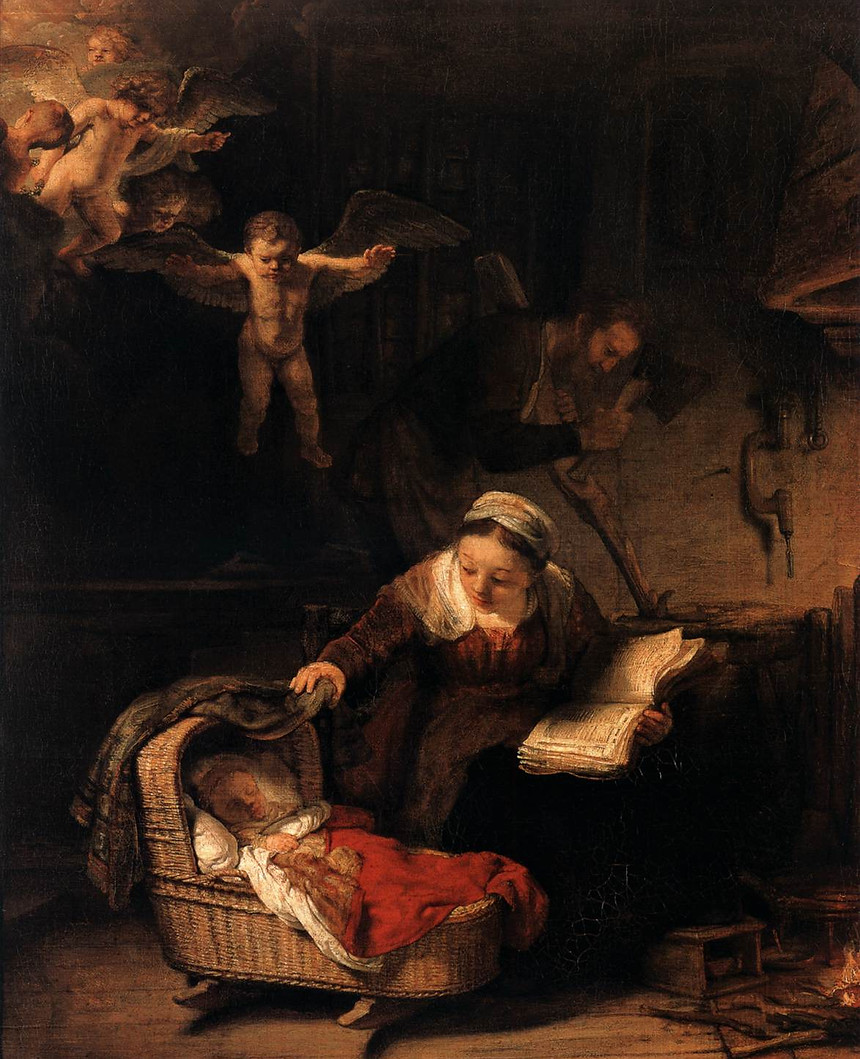

The Holy Family with Angels
1645

The Return of the Prodigal Son
c. 1669

Esther Preparing for the Meeting with Ahasuerus
c. 1633

The Angel Stopping Abraham from Sacrificing Isaac
1636

The Blinding of Samson
1636

Belshazzar's Feast
c. 1636

The Wedding of Samson
1638

David's Farewell to Jonathan
1642

The Toilet of Bathsheba
1643

Susanna and the Elders
1647

Bathsheba at her Bath
1654
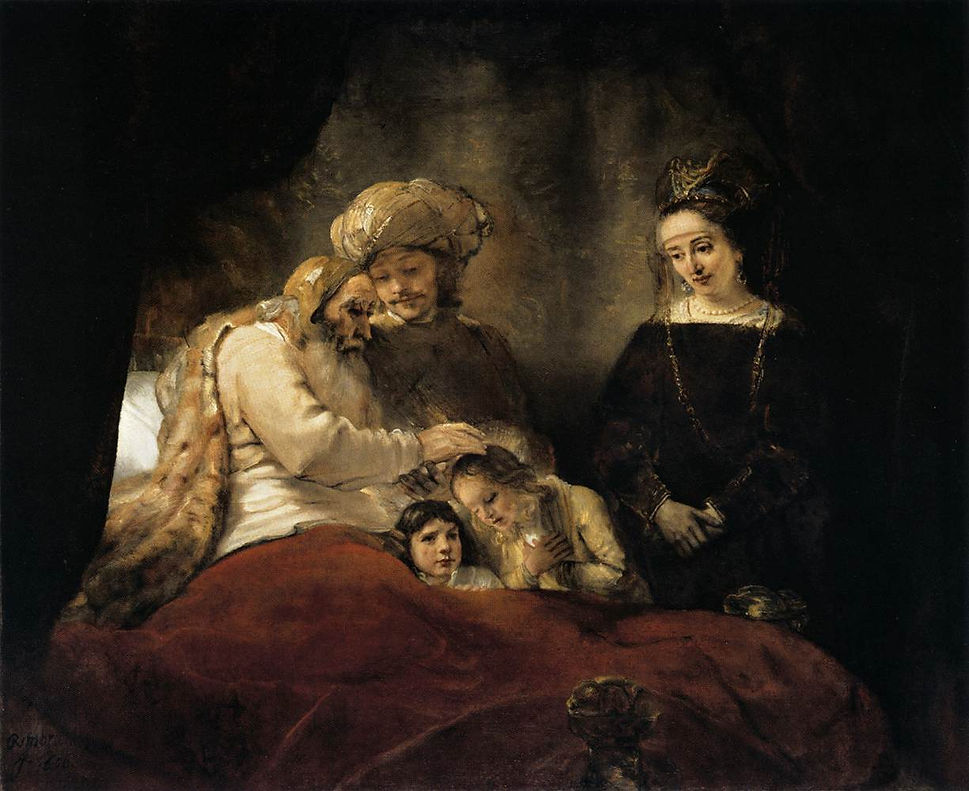

Jacob Blessing the Children of Joseph
1656

Saul and David
c. 1655

Moses Smashing the Tablets of the Law
1659

David and Uriah
1665

Minerva in her Study
1635

Abduction of Ganymede
1635
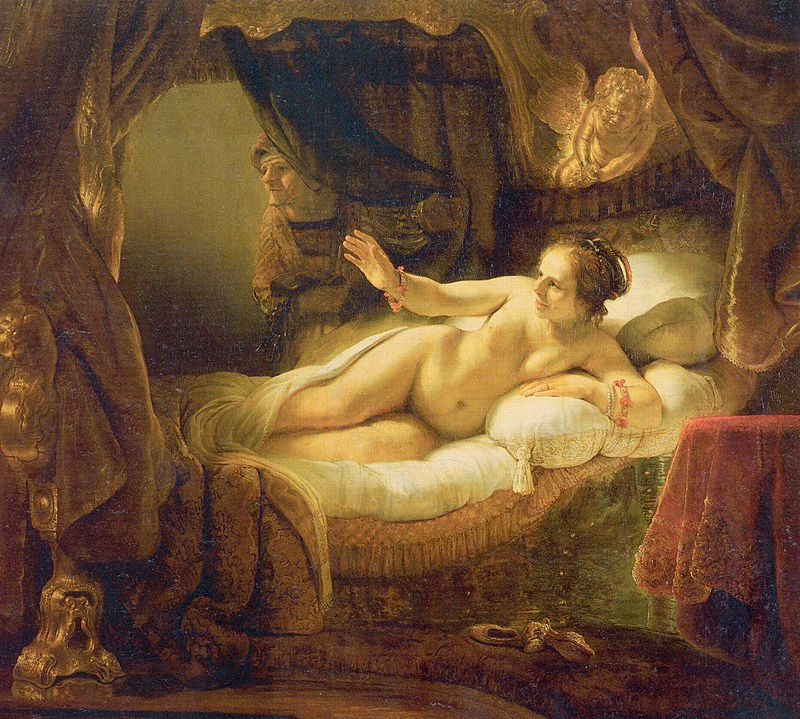

Danaë
1636

Juno
c. 1658
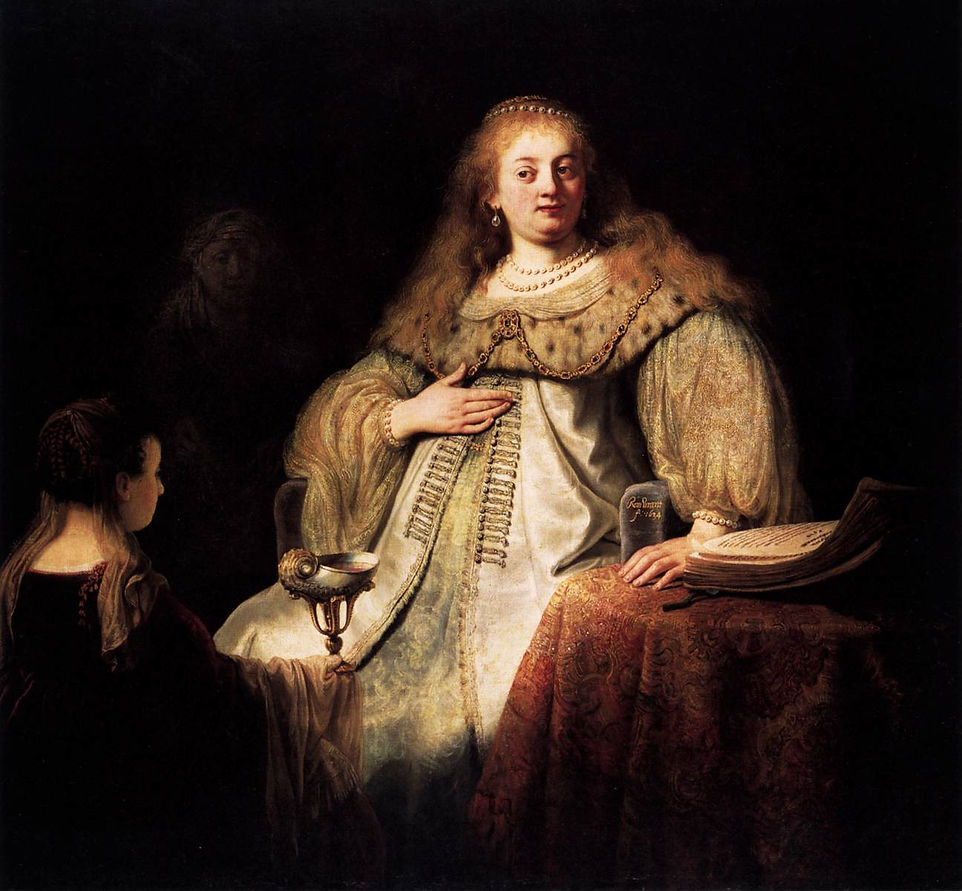

Artemisia
1634
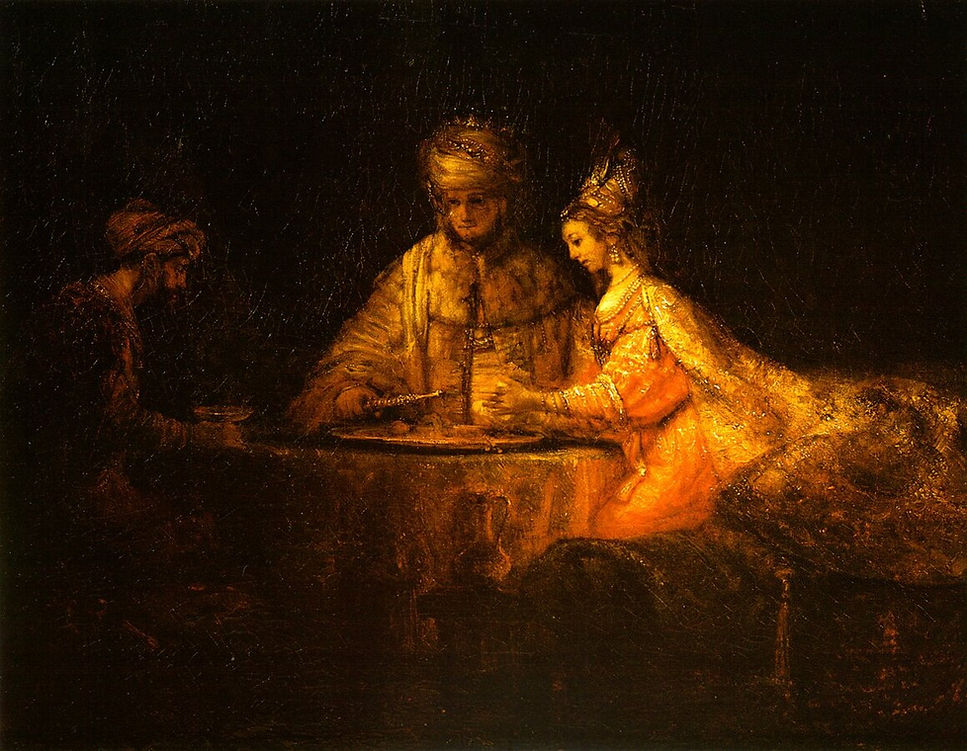

Ahasuerus and Haman at the Feast of Esther
1660
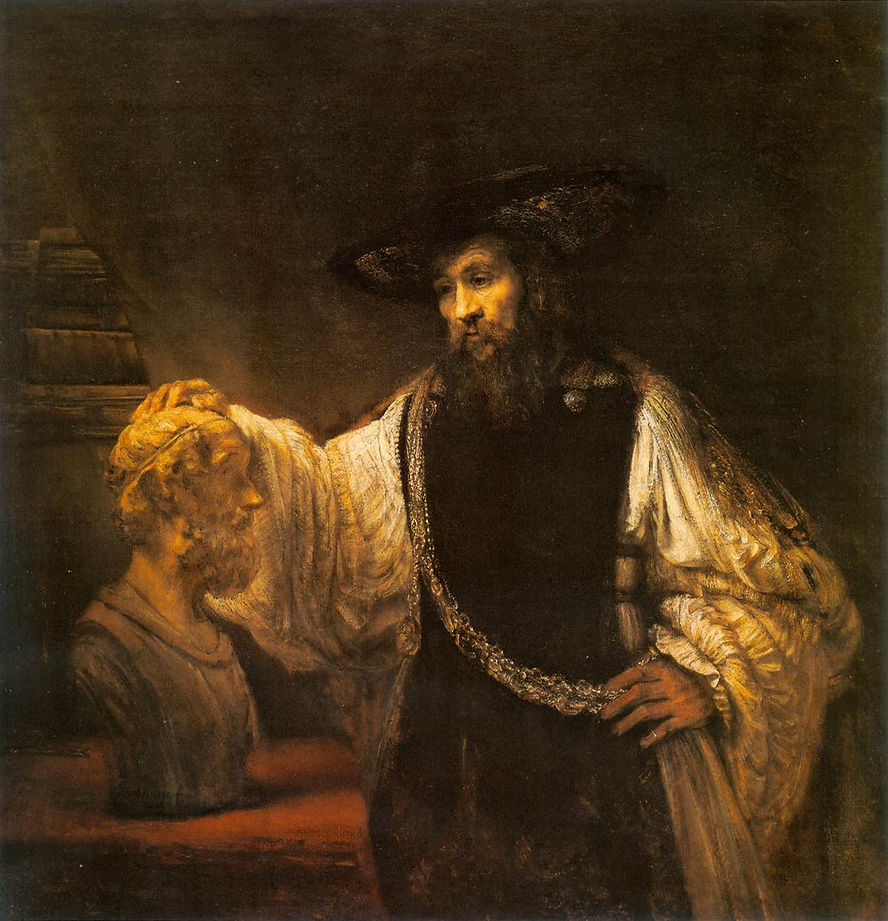

Aristotle with a Bust of Homer
1653
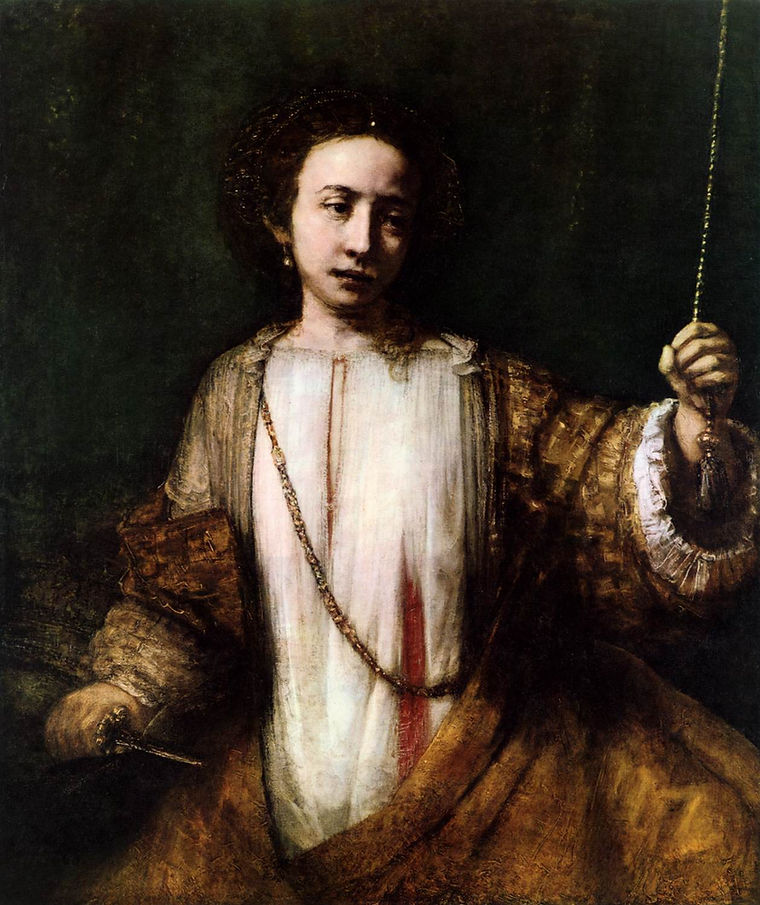

Lucretia
1666

Portrait of the Young Saskia
1633

Saskia as Flora
1634

Saskia van Uylenburgh in Arcadian Costume
1635

Rembrandt and Saskia in the Scene of the Prodigal Son in the Tavern
c. 1635

Hendrickje in Bed
1648

Portrait of an Old Man in Red
1652-54

Hendrickje Stoffels Bathing
1654
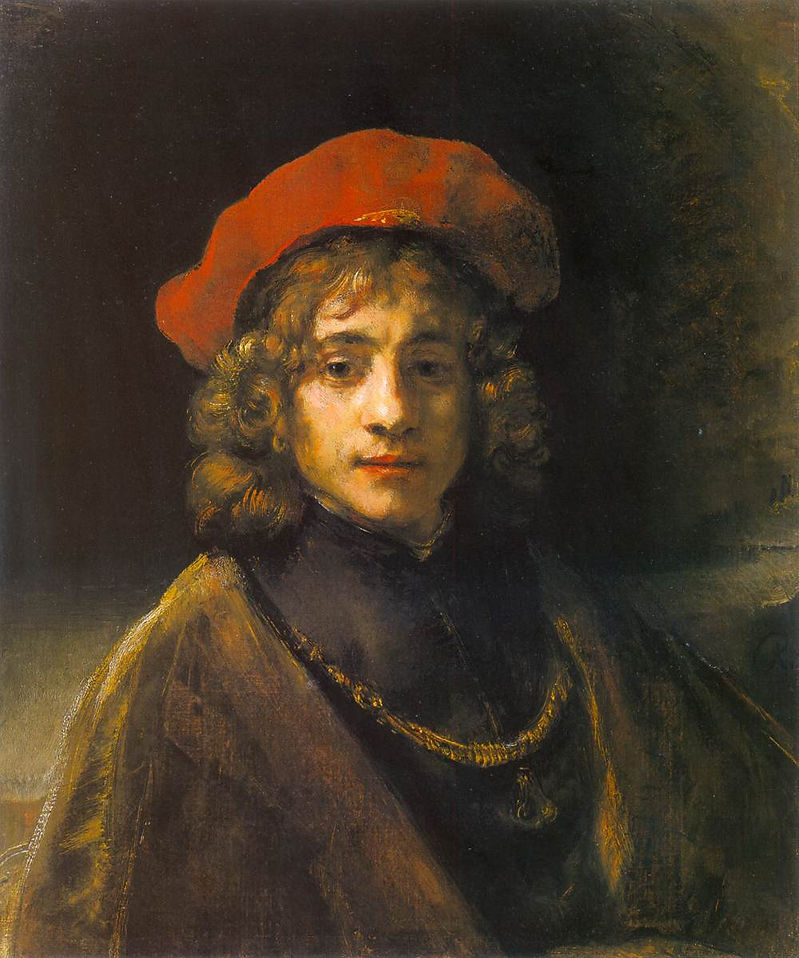

The Artist's Son Titus
c. 1657

The Jewish Bride
c. 1665
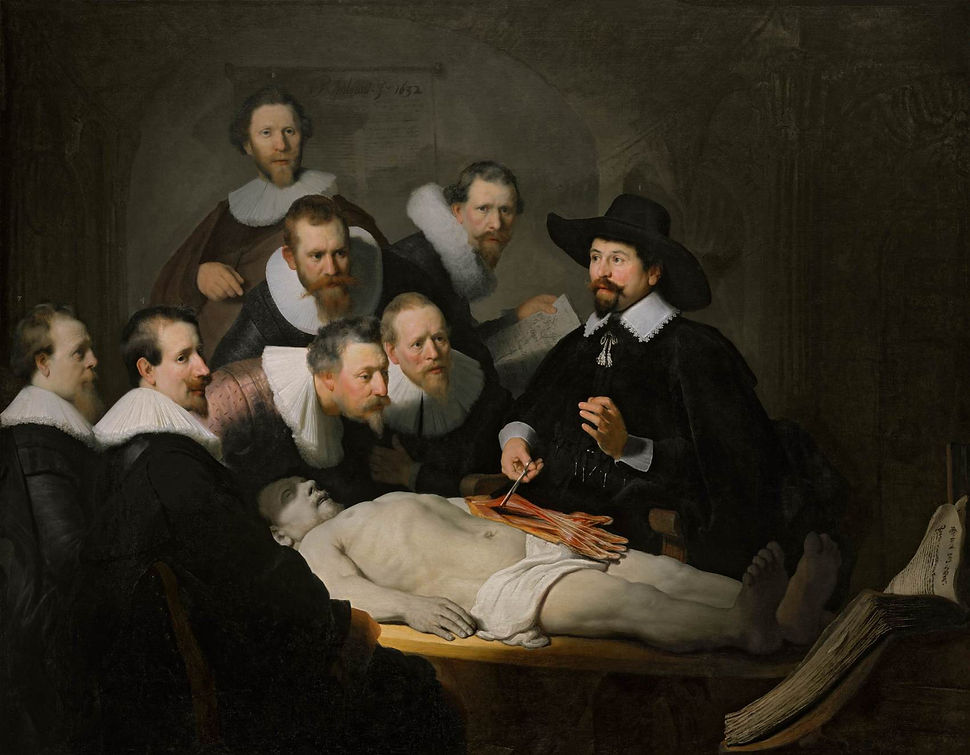
The Anatomy Lecture of Dr. Nicolaes Tulp
1632

The Nightwatch
1642

Self Portrait as Zeuxis
c. 1662
David Teniers
1610 – 1690
David Teniers the Younger or David Teniers II (bapt. 15 December 1610 – 25 April 1690) was a Flemish Baroque painter, printmaker, draughtsman, miniaturist painter, staffage painter, copyist and art curator. He was an extremely versatile artist known for his prolific output. He was an innovator in a wide range of genres such as history painting, genre painting, landscape painting, portrait and still life. He is now best remembered as the leading Flemish genre painter of his day. Teniers is particularly known for developing the peasant genre, the tavern scene, pictures of collections and scenes with alchemists and physicians.
He was court painter and the curator of the collection of Archduke Leopold Wilhelm, the art-loving Governor General of the Habsburg Netherlands. He created a printed catalogue of the collections of the Archduke. He was the founder of the Antwerp Academy, where young artists were trained to draw and sculpt in the hope of reviving Flemish art after its decline following the death of the leading Flemish artists Rubens and Anthony van Dyck in the early 1640s. He influenced the next generation of Northern genre painters as well as French Rococo painters such as Antoine Watteau.

Portrait of David Teniers by Philip Fruytiers
1655

Archduke Leopold Wilhelm in his gallery in Brussels
c. 1647–1651

Archduke Leopold Wilhelm in his gallery in Brussels
1650–52

A picture gallery with two men examining a seal and a red chalk drawing, and a monkey present

Archduke Leopold Wilhelm of Austria in his Gallery
1651

The Gallery of Archduke Leopold in Brussels
1639

The Gallery of Archduke Leopold in Brussels
1640

The Gallery of Archduke Leopold in Brussels
1641

Apes in the Kitchen
c. 1645

Smoking and drinking monkeys
c. 1660

Twelfth-night (The King Drinks)
1634-40

Dulle Griet (Mad Meg)
1640s

Temptation of St Anthony
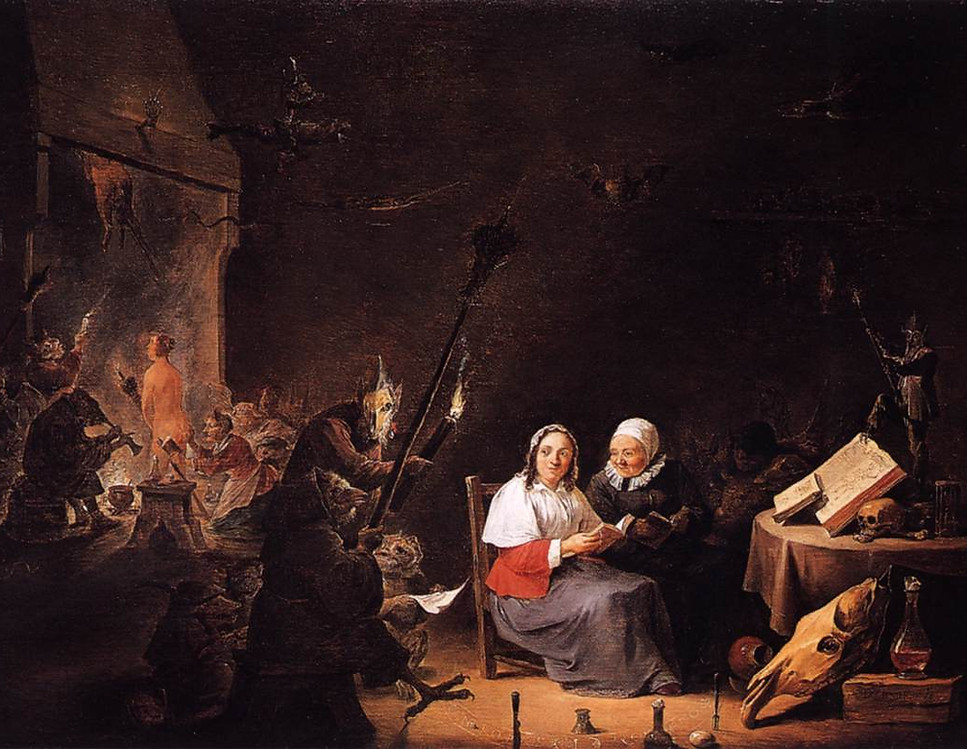

Witches' Initiation
1647-49
Jacob van Loo
1614 – 1670
Jacob van Loo (1614 – 26 November 1670) was a painter of the Dutch Golden Age, chiefly active in Amsterdam and, after 1660, in Paris. Van Loo is known for his conversational groupings; particularly his mythological and biblical scenes generally attributed to the genre of History painting. He was especially celebrated for the quality of his nudes to the extent that, during his lifetime, particularly his female figures were said to have been considered superior and more popular than those of his Amsterdam contemporary and competitor Rembrandt. In 1663, three years after fleeing to Paris, Jacob van Loo was accepted into the Académie royale de peinture et de sculpture.
Though his father also painted, Jacob's success ensured that he would forever be referred to as the founder of the Van Loo family of painters; a dynasty which was influential in French and European painting from the 17th to the beginning of the 19th century.

Self-portrait of Jacob van Loo
ca. 1660.

Meebeeck Cruywagen Family
c. 1640-45

A concert
1652

Danaë
after 1640

Melancholy
after 1660

Young woman going to bed
c. 1650

Naked Man and Woman
1650
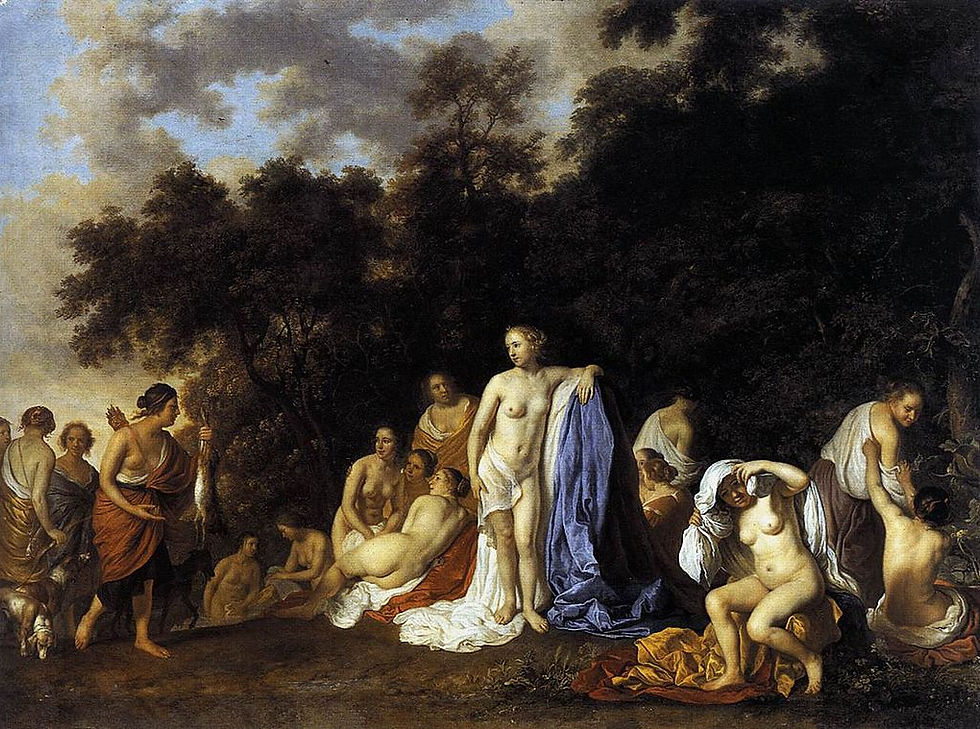

Diana and her Nymphs
1654

Danae
1650

Bacchic Scene
1653

Diana and her nymphs
1648
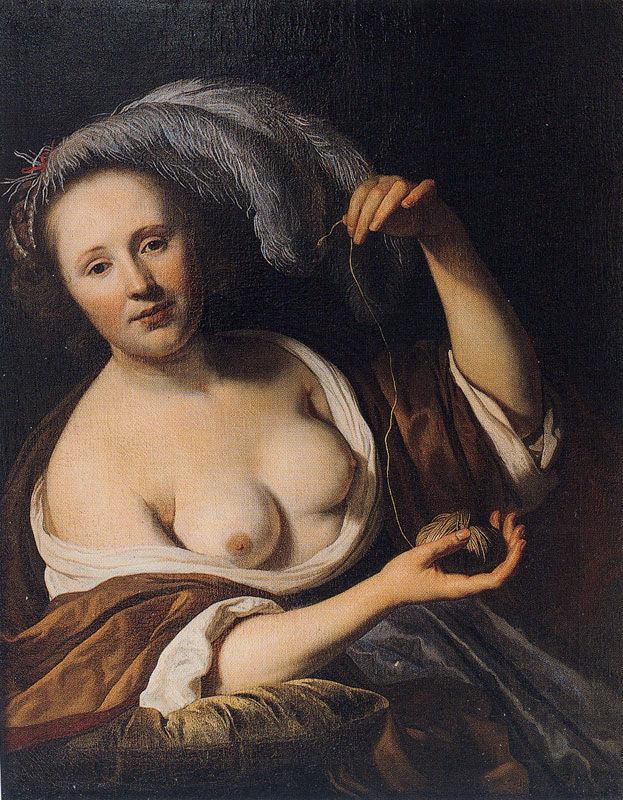

Ariadne
1652
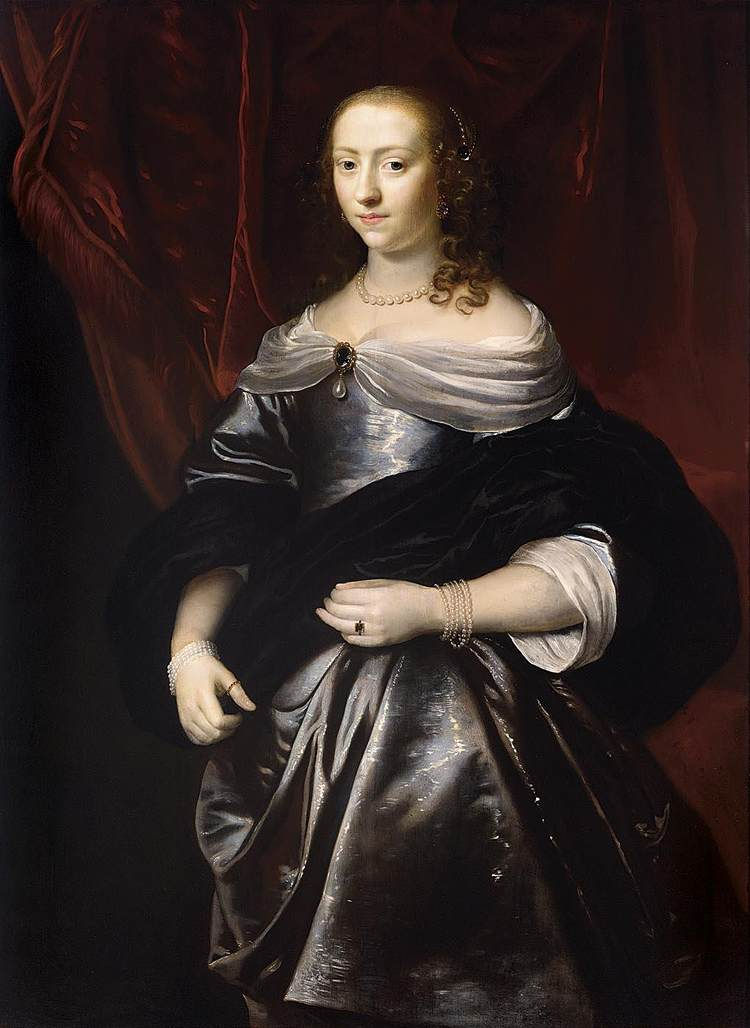

Portrait of Lucretia Boudaen

Portrait of a Couple
1657-58

Lot and his Daughters

Portrait of a Boy

A mother and son as Venus and Cupid

Boy with his dog

Bathsheba at her bath

Diana and her nymphs

Cimon and Ighigenie

Woman and child

Bacchanal

Silvio and the Wounded Dorinda
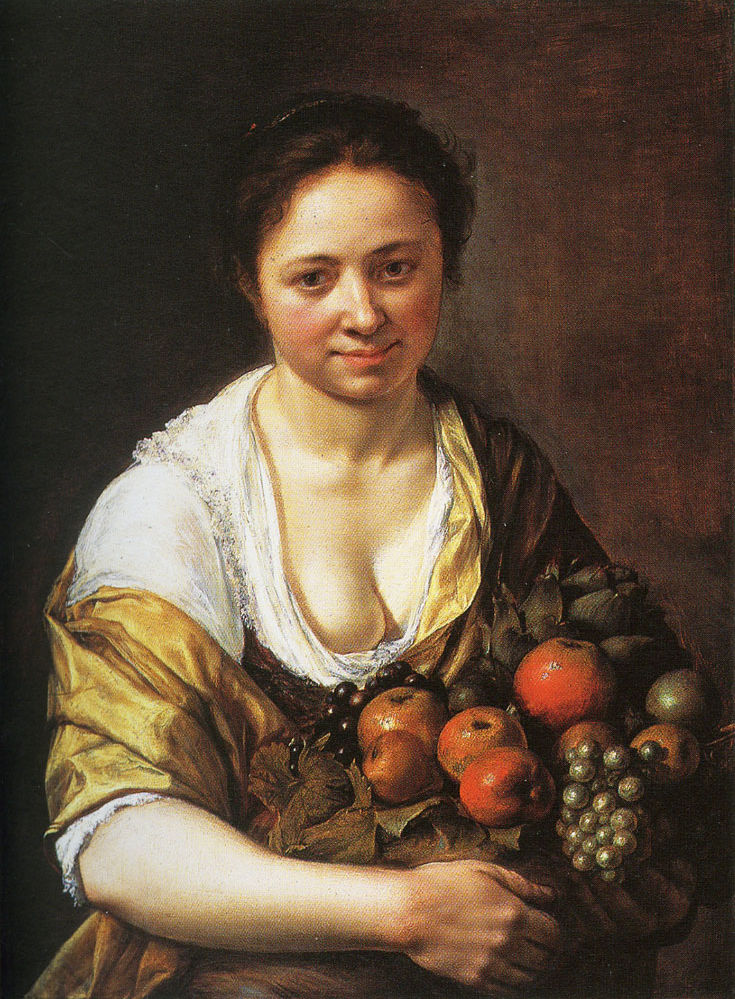

Girl with fruit

Portrait of a woman
Gerard Terborch
1617 – 1681
Gerard ter Borch (Dutch: [ɣəˈrɑrtɛr ˈbɔr(ə)x]; December 1617 – 8 December 1681), also known as Gerard Terburg, was a Dutch genre painter who lived in the Dutch Golden Age. He influenced fellow Dutch painters Gabriel Metsu, Gerrit Dou, Eglon van der Neer and Johannes Vermeer. According to Arthur K. Wheelock Jr., Ter Borch "established a new framework for subject matter, taking people into the sanctum of the home", showing the figures' uncertainties and expertly hinting at their inner lives. His influence as a painter, however, was later surpassed by Vermeer.
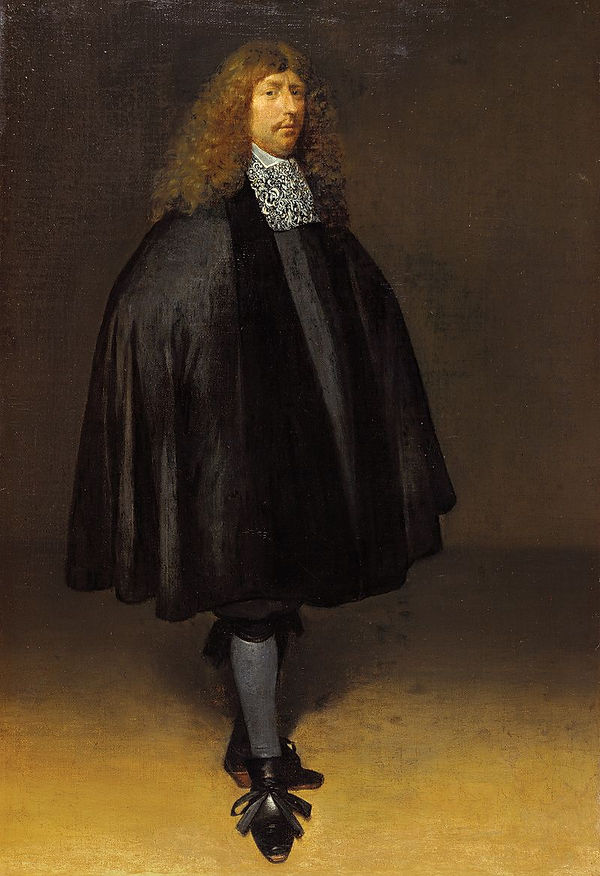

Self-Portrait

Paternal Admonition
1654-55

The Concert
c. 1657

The Van Moerkerken Family
1653-54

The Glass of Lemonade
1655-60

The Letter
c. 1655

Woman Peeling Apple
1650

The Suitor's Visit
c. 1658

Woman Playing the Theorbo-Lute and a Cavalier
c. 1658

Curiosity
c. 1660

The Dancing Couple
c. 1660

Lady at her Toilette
1660

A Woman Spinning
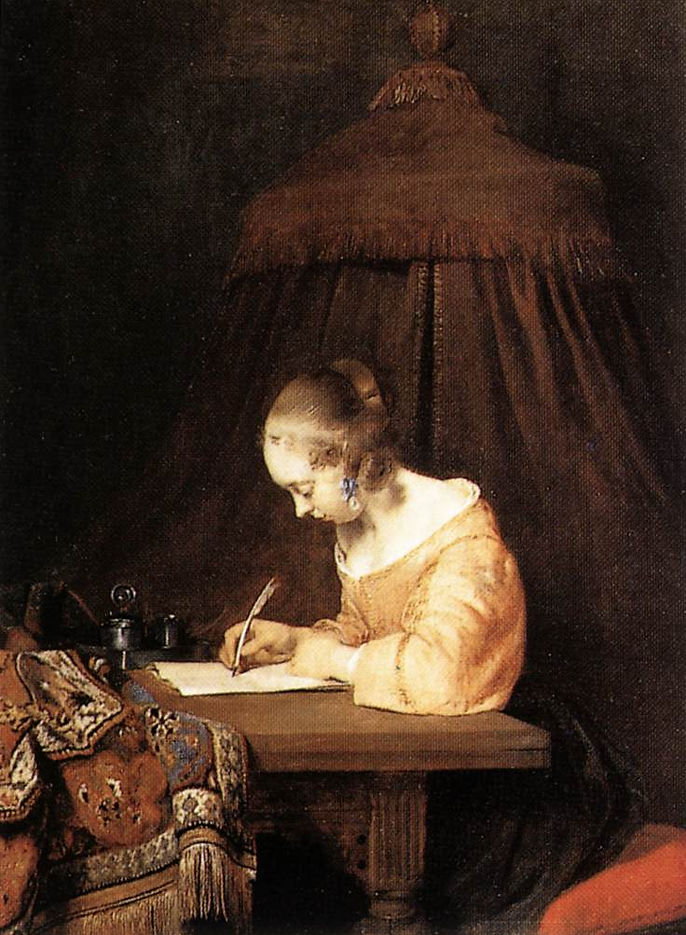

Woman Writing a Letter
c. 1655

Woman Drinking Wine
1656-57

A Concert
c. 1675
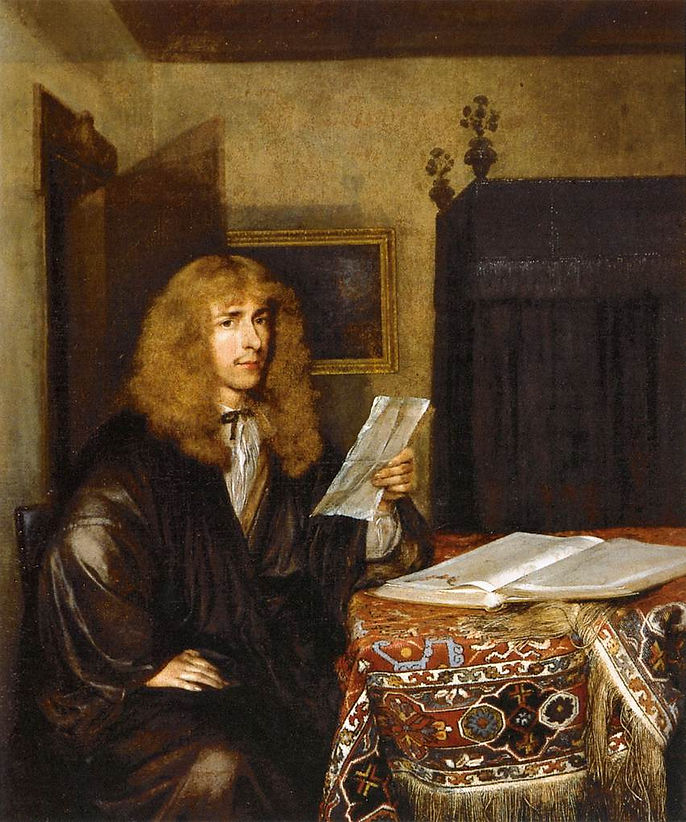

Portrait of a Man Reading
c. 1675

Man Offering a Woman Coins
1662-63

A Young Woman Playing a Theorbo to Two Men
1667-68
